Abstract
People are cognate beings living in a digital world, facing a quantum future, and the Internet of Things (IoT) is one thing that connects everything in the smart world. As a result, the biggest challenge faced by researchers is to minimize the energy consumption of these IoT technologies. The digital world is developing with such force and such a pace that you simply can't ban or control it. Taking inspiration in achieving low power consumption IoT, a GIoT is proposed. On the other hand, innovative technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) provide enhanced customer experience, drastic reduction in costs for the institutions, and increased profit margin which is of utmost importance considering the cutthroat competition in the market. In this chapter, we aim to share an overview as to how the institutions in the banking industry are making use of GIoT and its life cycle. Also, we would and how to leverage the power of AI and ML in the banking industry. More so, this article has scrutinized the important role of AI and ML in the banking sector and identified the latest technologies which can be adopted for reducing the carbon footprints because of the IoT.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Green Cloud Computing (GCC), Green Data Center (GDC), Green Internet of Things (GIoT), Green Wireless Sensor Networks (GWSN), hazardous emissions, Internet of Things (IoT), Machine Learning (ML)
11.1 Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) is being termed as the judicious tool which will help financial institutions, especially banks, to grow in the financial market which is the heart of the customer services industry [1]. Moreover, in the present unprecedented times, digital transformation is vital. The most important challenge at present is to update the legacy business software and revamp the existing banks without hindering the working system and the least inconvenience to the customer. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) come into the picture and play a crucial role in executing hassle- and risk-free digital migration [2].
IoT encompasses the projected growth network consumption and the number of nodes in the future. Hence, it is of utmost importance that the network components being used are reduced along with the reduction in the energy consumed in the entire process [3]. The world is transforming itself in terms of the processes used in having a Green IoT (GIoT). The process in itself is a state of the art that leads to a smart world implementation. The IoT should be known for its self-capacity to minimize the greenhouse effects and reducing carbon footprints. The smart world would become more sustainable only when the carbon dioxide (CO2) emission from the sensors, technology devices, applications, and services is automatically reduced [4]. When these changes are implemented the life cycle of the GIoT should have no impact on the environment concerning the Green Generation, Green Utilization, Green Architecture, and Green Disposal.
At present, there is enormous competition in the banking industry which has brought together the inherent pressure of managing the risk. Moreover, there is regulatory pressure in maintaining the standards of regulatory requirements and the government which the banks are required to improve. All this results in providing a different and unique customer service, which is pleasant.
11.2 Research Objective
The prime objective of this research is as given below:
- • To understand and study different ways in which the life cycle of GIoT can be adopted by the existing banking industry.
- • To understand how to maximize the inherent strength of AI and ML for working with data science acceleration this can be used for elevating the customers’ portfolio offerings in the banking sector.
- • To understand the major role of AI and ML in the banking industry.
- • To determine the modern technologies this can be embraced in developing methods for reducing the carbon footprints arising as a result of the IoT.
11.3 Methodology
We have used exploratory research design and collected secondary data to derive analogies concerning how GIoT can be deployed in the existing banking sector. Also, how we can leverage the inherent power of AI and ML in banking. External data has been collected from various websites for inspecting the major role of AI and ML in the banking sector. Upgraded and modern technologies have been identified for implementation in the banking sector which will, in turn, play a pivotal role in reducing the carbon footprints because of the Internet of Thing.
11.4 Result and Discussion
As time passed by, the average time spent by people on digital devices has increased manifolds. In terms of quantity, it ranges stupendously from millions to billions. Recent studies have projected that almost 75% of the world population having access to the internet; together connect more than 6 million devices along with an average of 4.5 billion people penetrating the internet in 2019 alone [5]. With the quantum of gadgets connected via the internet increasing, the IoT automatically becomes interesting. With the help of IoT data, banking institutions are at present developing various apps by assigning them to the various IoT developers. These apps end up transforming the banking experience of the customers. To partner with different business affiliates and FinTech services for embracing present-day demands and regulations while at the same time maintaining the security standards, this so-called AI and ML will play a pivotal role.
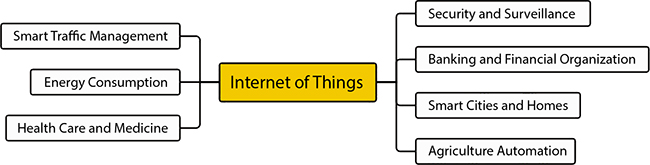
Figure 11.1 Some potential application domains of Internet of Things.
Few major application domains of IoT are highlighted in Figure 11.1. These are security and surveillance, banking and financial organization, agriculture automation, healthcare and medicine, energy consumption, smart traffic management, and smarts cities and homes.
11.4.1 Internet of Thing (IoT) in the Banking Industry
IoT can be defined as an interrelationship between solely referable and ingrained computing accessories within the current Internet framework. It is assumed that IoT will be able to provide the banking industry with a network of accessories, structure, system, and services which will go away from the routine machine-to-machine conversation along with enveloping an array of rules, domain and different functions [3]. The enormous traditional software and procedures which are present in the present banking and finance sector are bound to escort itself toward computerization because of these ingrained accessories. The banking and financial market is flooded with new commodities and new core strategies because of the conversion of data and process which is powered by the IoT [6]. This has resulted in a generation of new opportunities and process which will change the way the client interacts with the banks. A benchmark will be created for the banks to match and whichever entity fails to match the standards will end up losing the market share [7]. IoT contains the ability to define a new method of working with the existing systems in banking related to Know Your Customer, Credit Disbursement, Security Administration, Risk Controlled Self-Assessment, Forex Business, Alternate Delivery Channels, and Bank Assurance. With the help of other evolving automation in the market such as digital banking and biometrics, the IoT has the potential to develop innovative peer-to-peer business processes which can rattle the traditional money lending procedures in many places.
11.4.1.1 Internet of Things Facilitating Banking
An intelligent and robust system is formed when billions of devices are interconnected with each other. This is how the world is getting digitalized and modernized in every aspect. These intelligent systems transfer data using the cloud which is then scrutinized in different ways to help modify the businesses, the lifestyle of people, and the world in general [8]. As the lifestyle of the peoples change with modern technology and the smart devices they use in banking, the real-time details of the customer in terms of their finances are received by the banks. This vital data is shared by the bank from the customer’s side with the help of the various devices which the customers use. Effective use of this data enables the banks to project the customers’ needs and accommodate them with new solutions which, in turn, help the customer in making a correct decision with the effective use of their finances. Hence, the “Bank of Things” turns itself into a competent tool for adding value to the customer loyalty for the banks. This results in more business for the bank. In addition to this, banks also communicate with their customers through cell phones and provide the necessary guidance as per their needs. This results in a change in the behavior of the customers’ spending and purchasing habits. Banks can also build customer loyalty by communicating with them in various ways which may not necessarily be in finance but by offering advice and service in many spheres of life.
11.4.1.2 Benefits of Internet of Things (IoT) in Banking
IoT has numerous advantages when we talk in terms of banking. It provides value-added services to both its debt customers and credit card customers. Based on the patterns and volume of transactions through ATM kiosks by the customers, banks can either increase or decrease the number of ATMs in a particular area [9]. On the other hand, banks can also effectively use the IoT to introduce on-demand services by introducing need bases kiosks which can help in increasing the accessibility of banking services for the customer [7]. IoT can provide the banks with customer data which can, in turn, be utilized in identifying the business needs of the customers along with their preferred value chain of retailers, suppliers, and distributors [10]. This helps the bank in gaining customer insights. This vital information provided by the IoT supports the bank in introducing various value-added services, customized banking services and products, and need to be based on financial assistance to the customer. This ends up becoming a win-win situation for both the customer and the bank.
The IoT solutions have also been very beneficial in the agricultural sector for the farmers who are the customers of the banks. For instance, using modern technology the banks can project farming outputs in addition to the various other factors of crop farming. This has resulted in enabling the banks to forecast the output of the actual value of the crops being cultivated. With the help of the crop yield which is forecasted by the IoT, the banks are in a position to provide flexible financial benefits to the customers in terms of the conventional yield as well as the constancy and crop output. This results in developing a greater bond between the farmer and the bank.
Moreover, banks can also anticipate frauds in financial transactions and develop methodologies to prevent such occurrences beforehand [3]. Whenever a customer uses the card on a point of sale, the verified details of the customer flow to the bank through the device location. Now depending on the volume of the transaction and the concurrence of the customer the bank is in a position to confidently decline or process the transaction. Also, various sensor devices may be installed around the warehouses and storage points of the borrowers to note and track the inventory which flows in and out [11]. This crucial information can help the bank in monitoring the account which ensures that the credit taken by the customer is repaid promptly as and when the inventory is liquified by the customer. This results in reducing the manual tracking costs and denying the borrowers indulging in any dishonourable practices.
11.4.1.3 Other Benefits Benefits of the Internet of Thing (IoT) in Banking
The optimum application of connected devices can result in the customer taking a wise decision in changing the financial habits of overspending. As an example, one of the first IoT banks, Interact IoT, started implementing shock wearables as a constituent of an inculcation program for the users. As and when the customer sets a credit card limit, the wearable device would start tracking the spending habits every hour throughout the day and immediately raise an alert as and when the limit approaches. If the customer continues the spending without paying attention to the alert, then a shockwave is triggered by the wearable through the device on the wrists, indicating to the customer that the daily limit will be consumed shortly. That way, the user can take a cognitive approach toward the spending.
11.4.1.3.1 Improved Banking Experience
There are many ways in which the Internet of Thing affects the services provided in banking. It promptly provided customers with various insights and personalized exposure. The device connectivity with a network allows the customer to take a token beforehand and keep a check on it by using their smartphone. This provides them with a regular update with the exact time remaining for their turn in availing the service at the bank, rather than waiting in a line. The bank collects and stores the footfalls of the customers in their centralized database along with their preference of services which are utilized by them at the time of their bank visit. They also store the patterns of the questions being asked by them. This in return helps the bank customers to have an enhanced banking experience at every visit.
11.4.1.3.2 Expanded Range of Service Beyond Beyond Banking
At present, banks can make use of the IoT mechanism to broaden the variety of services and products available for their customers which are different from the regular features. For example, banks in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) have initiated fitness programs linked with their accounts with the bank which excites them to stay healthy. When the customers achieve a certain benchmark set by the bank they are rewarded in the form of a preferential rate of interest in accounts and free shopping vouchers. This process results in the customer thinking that the banks care about their fitness and, in turn, results in building a strong relationship with the bank.
11.4.1.3.3 Efficient Branch Banking
The public sector banks are finding it difficult to cater to branch banking in this era of mobile banking. The banks on one hand want to preserve the traditional system of banking which always used to add value to their business and old customers, whereas, on the other hand, to meet the ever-growing demands of the young generation, they have to make use of the technology where more emphasis is given to smart devices.
All the traditional banks are making full use of the IoT and other technology-driven banking applications to bridge this gap between the traditional banking at branch because of mobile banking [12]. For example, biometric sensors are being utilized to collect data whenever a customer enters the branch and transmit the same data to the primary system. Using the technology and creating lobby’s where all the IoT products are available in one single place the branches can reduce the number of employees and reduce the cost. This also results in reducing the turnaround time for the customer in availing the service. The back offices where the footfalls from the e-lobby are recorded can be used to link various branches in different locations.
11.4.1.3.4 Enhance Credit Card Ecperience
IoT has facilitated the evolvement of an interactive credit card. Instead of using the traditional plastic card, the customer talks and gets engaged with a digital display which allows them to strike a question to the bank branches in real-time and modify the features of the credit card upfront without any delay. Such instant modifications are very useful at the time of online shopping and other instant purchasing requirements.
11.4.2 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Banking
A recent survey by research conducting organization Autonomous Next has found out that banks around the globe can minimize the operating costs by around 22% by 2030 by effectively using technology driven by AI [13]. To minimize the frauds in the credit card sector, banks shall use face recognition technology which will then trigger an increase in the annual revenue growth by over 20% in 2021.
The extraordinary level of automation can be achieved with the effective use of AI and ML in reducing the repetitive and routine tasks done by humans by either taking over the human experts, or by intensifying their conduct while at the same time assisting them with the mundane jobs [14].
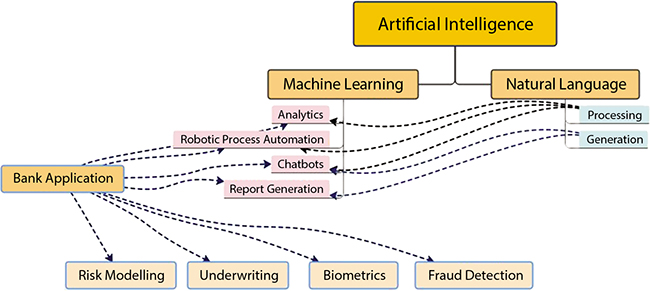
Figure 11.2 Artificial Intelligence in banking.
The different application in the banking sector where AI can be used effectively is mentioned above in Figure 11.2. Apart from these, there are many reasons behind the incorporation of AI and ML in the banking industry:
- • Heavy competition in the banking and financial industry.
- • Demand for process-driven services.
- • Introduction of customized service at banks.
- • Need for customized solutions.
- • Ensuring operational efficiencies.
- • Escalating employee efficiency.
- • Increase profitability and acquiescence.
- • To trim down maladies and safety risks.
- • To deal with a huge amount of business data.
- • To bring in effective decision making.
11.4.2.1 Significant Roles of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Banking and Finance
The extraordinary level of automation can be achieved with the effective use of AI and ML in reducing the repetitive and routine tasks done by humans by either taking over the human experts, or by intensifying their conduct while at the same time assisting them with the mundane jobs [15].
11.4.2.1.1 Mitigate Risk Management
Dealing with risk management is one area where the practical benefits of AI and ML can be demonstrated [16]. At the time of sanction and disbursement of credit limits to the clients, banks have to trust the creditworthiness of the customer by believing their history with them. In reality, the process is not smooth and correct every time, and the banks have to counter many challenges in approving the credit limits to the customer. With the advent of ML algorithms that analyzes and presents a better picture to the banks, the process of loan sanctioning has become much more convenient. This is the power of digital transformation.
11.4.2.1.2 Preventing Fraudulent Activities
Without any doubt, banks are looked upon as regulated institutions which are guided by strict government regulations and policies to prevent and safeguard financial frauds in the system [16]. It is no doubt that because of this reason it has become more important than ever for the banks to migrate in becoming complete digital as early as possible. The utmost important activity on the part of the banks is to be aware of the risks beforehand and not wait for any suspicious activity which may result in fraud. In the traditional process, banks were required to deviate from the set rules to avert fraudulent activity. ML technology can predict any doubtful movement even before the external hazard breaches the client's account. These tasks which are infeasible for humans to perform can be easily achieved by the machines by operating at high precision in real-time.
11.4.2.1.3 The Functionality of Chatbots
Chatbots are the latest AI and ML-based software that can clone human conversation. It becomes easier for the banks to reply to queries raised by the customer with the technology ingested chatbots and they have resulted in serving the banking sector on a large scale instantly.
11.4.2.1.4 Algorithm-Based Marketing
This technology of using algorithms to classify the client’s past actions and design special operation is a blessing for both the client and the bank. New age clients prefer such specially crafted services as it reduces their time and effort in searching for it manually as it brings all the necessary information directly to them. This augments their experience of banking.
11.4.2.1.5 Greater Automation and Improved Productivity
All the repetitive tasks can easily be taken over by AI and ML which, in turn, provides ample time for the staff to concentrate on many important and crucial tasks on hand. Full automation reduces manual jobs and eventually leads to higher profits.
11.4.2.1.6 Personalized Customer Service
When the tasks which have higher storage capabilities are automated, they provide a larger picture of the customers’ transaction habits and provide the most appropriate and personalized exposure. Effective use of the footfalls of the customer allows a bank to make the maximum use of the analytical capacity of AI and ML which helps in identifying the most ingenious tendencies in the customers’ action. This supports in creating a perfect personalized action for each customer.
11.4.2.1.7 More Precise Precise Risk Assessment
The staff who interact and work directly with the client can also benefit by minimizing the uncertainty when the correct digital footfall of each client is known. When it comes to scrutinizing the loan and avoiding any human mistakes, this automated system turns out to be more authentic than human intelligence.
11.4.2.1.8 Advanced Fraud Detection and Prevention
Without any doubt, the best feature of AI and ML in banking is to detect and prevent fraud from taking place beforehand because there is no dearth of criminals and innovative ways in which they commit fraud. Because of AI and ML at present, there are many ways in which we can identify and detect fraud before taking place.
11.4.2.2 Machine Learning for Safe Bank Transactions
Since the ML systems are continually learning, fraud avoidance in the financial institution is its. primary advantage [8]. If we have to put it in simple words, any same idea of committing fraud will never work in the same manner again. This work perfectly in the frauds committed with credit cards in banking institutions.
11.4.2.2.1 How Artificial Intelligence Makes Banking Safe
The prime spot nowadays where the financial transaction takes place is when the customer makes online spending, which makes it the perfect place for committing the fraudulent transaction under the influence of purchasing something. This fraudulent transaction can be prevented from taking place with the help of AI and ML. For instance, when a customer who is at a point of sale has a camera with face recognition then it can be used to identify the correct holder of the credit card. Moreover, in the frauds wherein discount coupons are offered with fraudulent intent, the Internet Protocol (IP) addresses can be easily tracked as and when the financial transaction takes place.
11.4.2.2.2 Market Research and Prediction
When ML is used in concurrence with big data, then it can assist in finding certain impressions along with assembling information. It becomes feasible to envisage currency variations, project the most profitable investment decisions, minimize risk, find the optimum position where the risk is lowest, identify the most perfect credit portfolio for the client, survey competitors, and identify security lapses.
11.4.2.2.3 Cost Reduction
The jobs done by the employees can be done more effectively with the help of ML which facilitates the financial institutions to predict deficiency in processes and organize it proficiently. For example, a chatbot can profitably handle the customers who have the most common and routine issues. Chatbots never demand any remuneration for their duty, in fact when we are working with ML it drastically cuts the costs of the institution. Without a doubt, it generates profit and raises the bar of customer service.
11.4.2.2.4 Machine Learning for Bank Transactions Monitoring
When it comes to keeping an eye on electronic payments and receipts, without a doubt, ML is far ahead of any other ground breaking technology [17]. ML is the ultimate solution to all future voluminous digital transactions [18]. Over the years in the existing traditional transaction system, it is difficult to set limits on the number of alerts. When the benchmark is set too low, if the institutions end up with a higher number of alerts then it demands scrutiny. When after setting the benchmark too high if the doubtful transactions are missed then the whole process of setting up alerts is of no use. The false alerts which look true at the first instance also require redressed as the effectiveness of the entire monitoring system depends on it. These tasks can be monitored and processed by humans only up to a certain level.
The ability to monitor financial transactions by ML in the banking industry is its most important feature. ML has proved to be very beneficial in discovering abnormality in financial transactions with many industries. ML can be very useful in fortifying the decision support system when offering a completely new automated analysis and examination, either by reinstating or assisting the expert [13]. This assistance can be in the form of security efficiency or operational efficiency.
11.4.3 Application of Machine Learning in Banking will Expand in 2021
Capital in billions is expected to be invested in the banking, finance, and insurance sector this year which is far ahead then the investment in other sectors [18]. Projections that were made in favour of AI and ML before the disastrous pandemic of Covid-19 have proven to be correct and the industry is deemed to grow more in the coming times.
11.4.4 Technologies that Can Be Adopted for Reducing Carbon Footprints
With the advent of technology and astounding growth in the area of the IoT, how we do our job and live our daily life has also changed. Even though the community has gained a lot from the benefits of the IoT, it has to be kept in mind that the Internet of T absorbs energy, brings in toxic pollution, and generates huge volumes of E-waste [19]. This thing puts a lot of pressure on nature and the smart world. This is why there is a huge appeal to shift toward the Green IoT to maximize its benefits and minimize the damage of the IoT. Green IoT is the environmentally benevolent future of the IoT [20]. This can be achieved by minimizing the CO2 footfalls, utilizing fewer reserves, and advocating competent techniques for using the available energy [21]. Hence, the electronic machines, communication devices, cloud storage, sensors, and internet have to be moved toward a Green IoT where the energy efficiency is improved and CO2 footprints are reduced.
With the internet, the whole world has become a small community wherein everything is connected and the entire world with the help of Global Communication Network using the TCP/IP Protocol [4]. The way we live our lives and communicate with different things including personal and professional affiliations is remarkably changed with the advent of the internet. Everything ranging from daily objects like home appliances, cars, motorbikes, electrical appliances, and communication devices are under the control of wireless communication networks. The IoT consists of smart connectivity of the present network and computation of awareness with ambience. Hence, the IoT is each and everything surrounding us which needs to be connected. In simple terms, it is anything that is connected to the internet. IoT technology makes all the instruments and machines smarter and enables them with the capability of storing and processing data brilliantly. IoT also makes technical communication between the instruments more adequate and accurate. Additionally, the IoT consists of an array of devices. It includes devices such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), sensors, smartphones, smart appliances, drones, and many more. These devices communicate with each other and work toward a mutual target of providing effective transmission [3]. Hence, many applications will foresee a wide change in their real-time recording and monitoring of data. A few of the applications which will undergo these changes are home automation, environmental and weather monitoring, e-healthcare, transportation sector, and industrial automation. Moreover, the IoT is also a boon for many applications which are in the area of wireless communications wherein brilliant handlers are deeply associated with the distribution of information, making collective decisions and completing jobs most favourably. IoT is nothing but the process of accumulating data, using data and its bilateral communication. IoT becomes omnipresent for big data which requires a huge capacity to store data, cloud computing (CC), and broad channel bandwidth for transmission [6]. Nonetheless, the processing of big data demands high power consumption which will indirectly put pressure on the surrounding environment and the society at large. Hence, to minimize carbon emission and reduce power usage, the Green IoT has been brought into the picture to accomplish the evolution of the smart world and its feasibility.
Keeping in mind the environmental damages taking place around the globe because of the CO2 footfalls, Green IoT initiatives needs to be given attention. Green IoT refers to the latest advancement in the modification of the IoT technology wherein the IoT is modified to become more environmentally friendly by utilizing the facilities and the storage capabilities which enables the users to collect, store, access, and supervise various collected information [22]. This modification in the existing technology and enabling for Green IoT is known as Information and Communication Technology (ICT). Green ICT means the storage capabilities which enable the users to collect, store, access, and supervise various collected information. This ICT can bring changes in the climate of the world at large primarily due to higher power and energy consumption. The present discussion on the stability of ICT has concentrated on data centers optimization, using different processes of allocation of framework and the infrastructure, which primarily maximizes energy competence. The focus should be on minimizing Carbon discharge and e-waste of material demolition. Greening ICT means enabling technology for the Green IoT which encompasses RFID, Green Cloud Computing (GCC), Green Data Center (GDC), green internet, and green communication network. Hence, Greening ICT plays a major role in the Green IoT and accommodates numerous benefits to the environment by minimizing the power and energy consumptions utilized for designing, manufacturing and distributing ICT accessories, machinery, devices, and types of equipment.
11.4.4.1 Green Internet of Things (Green IoT)
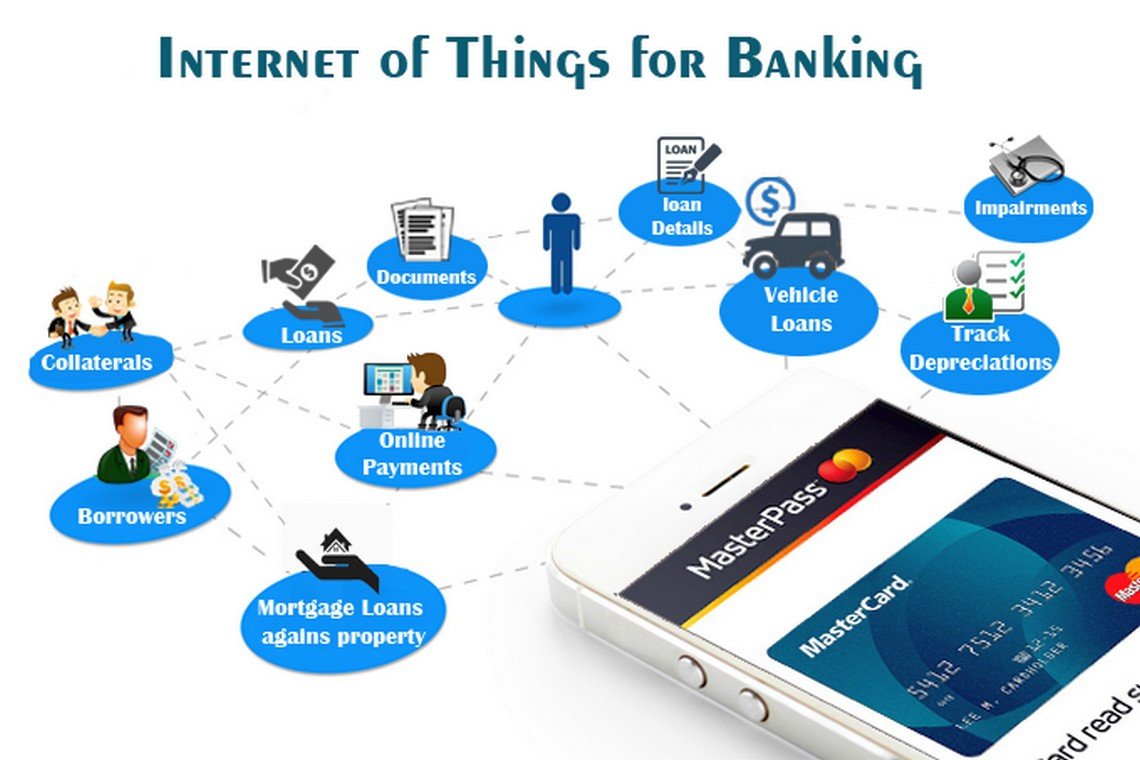
IoT encompasses an unseen communication chain and a computing ambience which is built on smart cameras, sensors, various software and data center which stores the entire data. Its scrutiny has embraced the possibility of utilizing the IoT for building a green grounds climate that is focused on energy saving. Notwithstanding earlier proof surrendered, IoT components were talked about in, where the upsides of IoT design concerning how to make green grounds by using the trend-setting innovations astutely and proficiently were portrayed [23]. The areas where GIoT should be incorporated in banking are as given in Figure 11.3.
Figure 11.3 Internet of things in banking.
Green Internet of ThingsIoT has three ideas, in particular, plan innovations, influence advancements, and empowering advances. Plan advances allude to the energy productivity of gadgets, correspondences conventions, network models, and interconnections. Influence advances allude to cutting fossil fuel by-products and upgrading the energy effectiveness [24]. Because of gres, the Green Internet of ThingsIoT turns out to be more proficient through lessening energy, decreasing dangerous emanations, diminishing assets utilization and diminishing contas, the Green Internet of ThingsIoT prompts saving regular assets, limiting the innovation sway on the climate and human wellbeing and decreasing the expense essentially.
11.4.4.2 Green Cloud Computing Technology
At present CC is fast materializing in a virtualization technology used across the internet. Limitless computational capacity, unrestricted storage capacity, and prompt service delivery through the internet come along with it [25]. CC is omnipresent, whereas the IoT is universal. CC and the IoT both go hand in hand in providing an enhanced research study [26]. The basic target of GCC has always been in advocating the usage and utilization of products that are eco-friendly and which can be easily recycled and reused without delay. Another aim of GCC is to minimize the hazardous nature of the materials being used, optimize and maximize the consumption of energy and increase the recyclability of the old products and the wastes being generated from them. Additionally, it can be achieved by product durability appropriation of resources and paperless virtualization. The same idea is supported by research and study in the field for GCC by minimizing energy utilization.
The main goal of GCC which is to reduce the carbon footprints is backed by utilizing numerous techniques and ideas to reduce the usage of power in its application [25]. The Public and Private Clouds were examined and they constituted energy consumption in switching, data processing, transposable, and data storage along with electronic data processing. In terms of the percentage of total energy utilization in CC, the actual energy utilization in transportation and circuit, switching forms a major chunk. GCC the optimum and likely solutions can be summarized as follows:
- (I) Acceptance of hardware and software for reducing energy utilization.
- (II) Power conservation by adopting VM techniques such as VM amalgamation, VM migration, VM placement, and VM allocation.
- (III) Different energy capable means allocation and mechanisms and tht risks.
- (IV) Capable and Productive productive methods for energy-saving systems.
- (V) GCC procedures positioned on CC backend technologies such as communications, network, etc.
11.4.4.3 Green Data Centre (GDC) Technology
The latest technology for data management, data dissemination, and data storage are commonly known as GDC [27]. The prime components of these data are users, systems, things, etc.
In the process of working with distinct and different data along with the various applications, the data center absorbs a substantial quantity of energy with high working cost and substantial releasing of carbon footprints [28]. Moreover, the production of big data is soaring by numerous universal things, namely, cell phones and sensors. With this path of moving toward a digital and smart world, the energy capability for data center becomes more compelling.
Additionally, GDC has a provision of accommodating the data services for cloud supported mobile ad-hoc networks in 5G. Progressive technologies are utilized for reducing the paints used in structures and carpets, a low emanation of building products, imperishable landscaping and utilizing substitute of regular form of energy like heat pumps, solar cells, and evaporative cooling [28]. The process of saving energy in data servers using cloud technology is reducing routing and searching transactions. Engineers have examined the mechanism combined capability into the energy capable context-aware broker framework (more commonly known as e-CAB) to govern next-generation data center. The examination has resulted in a GDC wherein the air conditioning is supported by cloud procedures and techniques wherein two sub-processes are there, namely: (1) Data Center of Air Conditioning System and (2) Cloud Management Platform. The prime function of the Ant Colony System was to search for a feasible clarification and solution. Additionally, the dynamic virtual machine is generally utilized for minimizing the energy and power consumption of the cloud data center while preserving the perfect Qualityof-Service. Hence, every device is utilized by multiple users and a virtual machine is utilized to access those physical devices.
11.5 Conclusion
With an increase in the popularity of the various online tools by the customers, the banks have been forced to utilize the IoT data with the intent to modify and upgrade their experience of banking with the new services and products. This is where the banks will have to leverage the power of AI and ML in banking along with data science acceleration to enhance customers’ portfolio offerings. In the present scenario, the banks need to convert the data generated from the IoT into information that gives them some value and which, in turn, can help them in making informed and qualified decisions. This will, in turn, help them in increasing their market share resulting in a pleasant experience of better services to the customer and this will be possible only with the help of the introduction of AI and ML in the banking sector. With this increased use of AI and ML, the utmost important thing will be to make the optimum use of the Green IoT which contains green design, green production, green utilization, and green recycling. Its effective use can result in reducing carbon footprints because of the IoT. This reduction in the carbon footprints will be beneficial for society and it has its benefits and its social implications and industrial implications for the society. Hence, the Green IoT means concentrating on Green Production, Green Usage, Green Architecture, and Green Demolition.
- • Green Production: Developing electronic peripherals and computers along with the correlated subsystems with minimum or no impact on the environment and society at large.
- • Green Usage: Reducing the energy consumption of computers and their peripherals and making their optimum use in an environmentally friendly manner.
- • Green Architecture: Energy-efficient designs for Green IoT sound peripherals, computers, and servers and its cooling technology.
- • Green Demolition: Remodeling and reusing old computers and recycling rejected computers and other electronic equipment.
Concerning ML, it was not going to take long for AI and ML to take hold in modern banking because of the rapid pace with which the technology is getting used in the banks. This has, in turn, redefined the existing dynamics existing in the banking industry forever. The data provided by AI and ML can be utilized and analyzed for forecasting consumer behavior in terms of patterned data sets of customers’ behavior and spending behavior. This will result in providing them with better services utilizing modern technology. The effective and early adoption of AI and ML will play a major role in providing the banks with a competitive edge with their peers and will ultimately result in providing a pleasant experience to their customers in terms of speed which will be fast, a trust which will be secured and banking experience which will be personalized.
References
1. León, O., Hernández-Serrano, J., Soriano, M., Securing cognitive radio networks. Int. J. Commun. Syst., 23, 5, 633–652, 2010.
2. Cioffi, R., Travaglioni, M., Piscitelli, G., Petrillo, A., De Felice, F., Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications in smart production: Progress, trends, and directions. Sustain., 12, 2, 1–26, 2020.
3. Kumar, S., Tiwari, P., Zymbler, M., Internet of Things is a revolutionary approach for future technology enhancement: a review. J. Big Data, 6, 1, 1–21, 2019.
4. Byoung-Oh, G., Kim, T.C., Yang, S.E., A Study on Internet of Things Implementation. J. Knowl. Inf. Technol. Syst., 12, 6, 845–856, 2017.
5. Kemp, S., DIgital2019: Global Digital Overview, 2019. https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2019-global-digital-overview, 2019.
6. Hussein, A.R.H., Internet of Things (IOT): Research challenges and future applications. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl., 10, 6, 77–82, 2019.
7. Malali, A.B. and Gopalakrishnan, S., Application of Artificial Intelligence and Its Powered Technologies in the Indian Banking and Financial Industry: An Overview. IOSR J. Humanit. Soc Sci. IOSR-JHSS, 25, 6, 55–60, 2020.
8. Kaur, N., Sahdev, S.L., Sharma, M., Siddiqui, L., Banking 4.0: ‘The Influence of Artificial Intelligence on the Banking Industry & How Ai Is Changing the Face of Modern Day Banks’. Int. J. Manag., 11, 6, 577–585, 2020.
9. Salunkhe, R.T., Role of Artificial Intelligence in Providing Customer Services with Special Reference to SBI and HDFC Bank. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng., 8, 4, 12251–12260, 2019.
10. Pareek, A., Internet of Things (IoT) in Banking: Examples of IoT Solutions In Finance, https://customerthink.com/internet-of-things-iot-in-bankingexamples-of-iot-solutions-in-finance/, 2020.
11. Adam, A., Internet of things in the supercool game of B2B marketing, 2017. https://customerthink.com/internet-of-things-in-the-supercool-gameof-b2b-marketing/, 2017.
12. Vijai, C., Artificial Intelligence in Indian Banking Sector: Challenges and Opportunities. Int. J. Adv. Res., 7, 4, 1581–1587, 2019.
13. Chuprina, R., Machine Learning in Banking – Opportunities, Risks, Use Cases, https://spd.group/machine-learning/machine-learning-in-banking/, 2021.
14. Shouval, R., Fein, J.A., Savani, B., Mohty, M., Nagler, A., Machine learning and artificial intelligence in haematology. Br. J. Haematol., 192, 2, 239–250, 2021.
15. Das, P., AI and Machine learning are redefining the banking industry, https://www.analyticsinsight.net/ai-machine-learning-redefining-bankingindustry/, 2020.
16. Leo, M., Sharma, S., Maddulety, K., Machine learning in banking risk management: A literature review. Risks, 7, 1, 1–22, 2019.
17. Dey, A., Machine Learning Algorithms: A Review. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol., 7, 3, 1174–1179, 2016.
18. Carbo-Valverde, S., Cuadros-Solas, P., Rodríguez-Fernández, F., A machine learning approach to the digitalization of bank customers: Evidence from random and causal forests. PLoS ONE, 15, 10, October, 2020.
19. Baliga, J., Hinton, K., Ayre, R., Tucker, R.S., Carbon footprint of the internet. Telecommun. J. Aust., 59, 1, 05.1–05.14, 2009.
20. Ferrag, M.A., Shu, L., Yang, X., Derhab, A., Maglaras, L., Security and Privacy for Green IoT-Based Agriculture: Review, Blockchain Solutions, and Challenges. IEEE Access, 8, 32031–32053, 2020.
21. Uddin, M., Okai, S., Saba, T., Green ICT framework to reduce carbon footprints in universities. Adv. Energy Res., 5, 1, 1–12, 2017.
22. Alsamhi, S.H., Ma, O., Ansari, M.S., Meng, Q., Greening internet of things for smart everythings with a green-environment life: A survey and future prospects. arXiv, 1–14, 2018.
23. Gadre, M. and Gadre, C., Green Internet of Things (IoT): Go Green with IoT. Iciot - 2016, 4, 29, 1–6, 2016.
24. Bashar, D.A., Review on Sustainable Green Internet of Things and Its Application. IRO J. Sustain. Wirel. Syst., 1, 04, 256–264, 2019.
25. Atrey, A., Jain, N., Iyengar, N.C.S., A Study on Green Cloud Computing. Int. J. Grid Distrib. Comput., 6, 6, 93–102, 2013.
26. Chowdhury, C.R., Chatterjee, A., Sardar, A., Agarwal, S., Nath, A., A Comprehensive study on Cloud Green Computing: To Reduce Carbon Footprints Using Clouds. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Res., 3, 8, 78–85, 2013.
27. Varde, A., Robila, S., Michael, P., Energy Green Data Centers for Sustainability White Paper. Technol. Innov. Progr. (TIP) Natl., Usepa, 2007, 2011.
28. Uddin, M. and Rahman, A.A., Techniques to implement in green data centres to achieve energy efficiency and reduce global warming effects. Int. J. Glob. Warm., 3, 4, 372–389, 2011.