 Data is the most critical asset for any organization. As companies have continued to expand, their need for information storage and access has expanded exponentially, and there is no end in sight to the need for data storage and retrieval. By now, most organizations have moved from files and folders to the database. The relative ease of use and efficiency of the database accounts for its success in taking on the majority of companies’ important data. The database offers a placeholder for storing information, but more importantly, when properly organized, it allows for efficient and meaningful information retrieval.
Data is the most critical asset for any organization. As companies have continued to expand, their need for information storage and access has expanded exponentially, and there is no end in sight to the need for data storage and retrieval. By now, most organizations have moved from files and folders to the database. The relative ease of use and efficiency of the database accounts for its success in taking on the majority of companies’ important data. The database offers a placeholder for storing information, but more importantly, when properly organized, it allows for efficient and meaningful information retrieval.
A database management system (DBMS) is the software that controls the storage, organization, and retrieval of data. A relational database management system (RDBMS), as defined by Codd’s Rules, adapts to the relation model with well-defined object stores or structures. These stores and structures, commonly known as operator and integrity rules, are clearly defined actions meant to manipulate and govern operations on the data and structures of the database.
NOTE
Oracle introduced the first commercially available RDBMS database in 1979, with Oracle V2 (Version 2). Oracle Database has evolved far beyond RDBMS through continuous innovation. With every new version, Oracle introduced new features. In 1999, Oracle introduced Oracle8i (i in 8i stands for Internet), a database designed for Internet computing that can be deployed in a multitier environment. In 2001, Oracle9i introduced a breakthrough in Oracle technology, Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC). RAC made it possible to access the same database from multiple instances simultaneously, making Oracle Database highly available. In 2003, Oracle10g (g in 10g stands for grid) introduced grid computing, which emphasized creating a farm of low-cost commodity servers (grid infrastructure) and running Oracle Database on the same. Oracle11g introduced Active Data Guard, which enabled a standby database to be open in read-only mode for reporting purposes.
Oracle Database 12c brings the database to a cloud-ready state. Oracle12c introduces two new groundbreaking features:
Multitenant database architecture This enables an Oracle Database to function as a multitenant container database (CDB) that can include a single pluggable database (PDB) or multiple pluggable databases.
Oracle Database In-Memory, transparently accelerates analytic queries by orders of magnitude, enabling real-time business decisions; it also speeds up operational transactions in a mixed workload environment. Embedding the In-Memory capabilities into the existing Oracle Database software ensures that it is fully compatible with all existing features and requires no changes in the application layer.
Before we dive directly into discussing Oracle Database In-Memory, let’s first take a look at the architecture of an Oracle database.
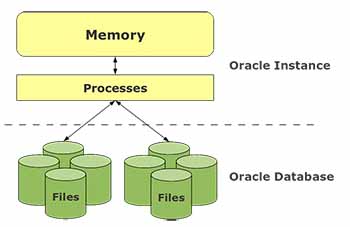
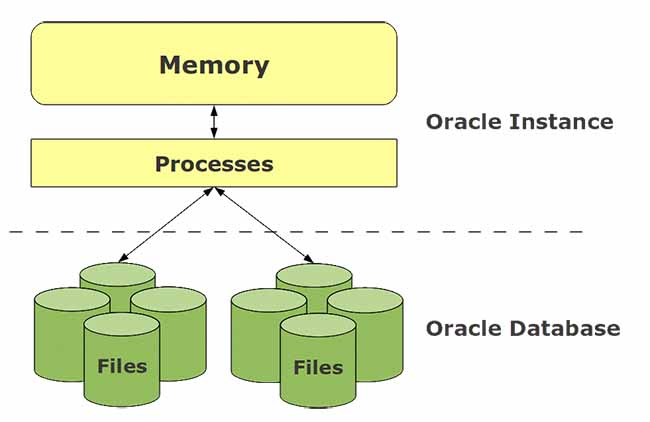
In simplest terms, a database consists of physical files that store the entire data and instance. An instance includes a set of memory structures and background processes that manage the physical files. The physical files that store data are sometimes also referred to as the database.
Oracle database server = physical files + instance
Or
Oracle database server = database (physical files) + instance
A database can comprise three major structures:
- Storage structure
- Memory structure
- Process structure
The storage structure consists of physical storage (or physical files) and logical storage (the logical distribution of data). Logical storage is in the form of a table, index, tablespace, and so on and helps to manage the physical structure effectively. We will study this in detail in the next section.
Although the storage structure is part of the database, memory structure and process structure are part of the instance as well.
A database can have one or more than one instance. A database with only one instance is called a single-instance database. If the database has more than one instance and if all the instances access the same database simultaneously, it is called a Real Application Cluster (RAC) database. By default, an RAC database is always active-active. If two database instances are configured and only one remains active at any point in time, it is known as active-passive configuration. Oracle Database supports both active-active and active-passive configurations. Oracle Database 12c also introduces CDBs and PDBs.
An instance can access only one database at any point in time. Though a database can have multiple instances (RAC), an instance cannot access multiple databases at the same time. Thus, an instance is mapped only to one database at a particular point in time. An instance can be present without the database, and vice versa. Normally, when you create a database using the create database command, the instance is there but not the database. Similarly, when you have the backup of a database, you have only the physical files, which constitute the database but not the instance. In order to have a working database, you need both the database and an instance.

